Through the elimination of harsh and pollutant heavily chemical, our ozone sanitation technology provides an innovative, environmentally friendly, and more sustainable method to sanitize various surfaces and equipment.
Currently being used in industries including food production, military and first responders, water treatment, breweries and more. Nebula’s ozone technology can improve efficiency and effectiveness by eliminating cleaning solutions that are harmful to you, your customers, and the environment.
- Cleaning and sanitizing with one application
- A safer, healthier path to clean!
- Converts back to air and water, reducing your carbon footprint
- Once attached to the contaminants the ozone solution eliminates them, converting back to air and water
Oxidation Reduction Potential [ORP]
In the cleaning and sanitization industry there are several different terms of measurement to consider. Cleaning Units is measured by the equation PSI x GPM or as Cleaning Units/Hour <PSI x GPM x Hrs>. These terms can be found when looking at power washer specs in understanding the flow and pressure delivered by a machine. That is to say that the pressure being applied by the washer in Pounds-per-Square Inch and the flow in Gallons Per Minute over a certain duration is the cleaning unit measurement. Whether the pressure being applied is 2000, 3000, or 4000 PSI makes a big difference in ability to properly remove contaminants and other undesirable materials from surfaces that are being cleaned.
Heat Heat is another variable that can largely impact the cleaning ability of a solution. Especially in applications where oils, greases, or resin is involved the heat applied helps break things down and allows the cleaning solution to do its task more effectively.
Water Water dissolves more substances than any other solvent including acids and bases. The pH or potential of Hydrogen is the measurement of acidity or alkalinity of a substance dissolved in water. Pure water has a pH of 7 or neutral on the scale of 1 to 13.
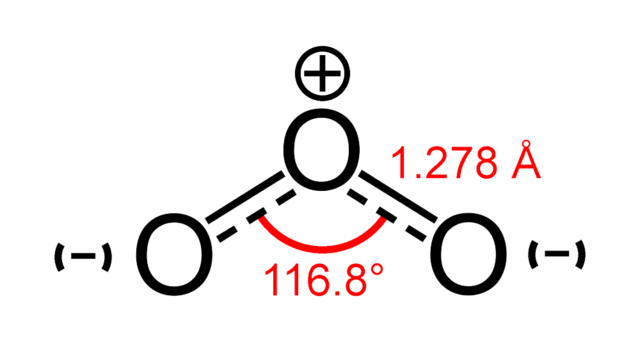
Chlorine, Chlorine Dioxide, Peroxide, and other disinfectants’ cleaning power is measured in Oxidation-Reduction Potential or ORP. It is a measurement of electro-chemical potential ranging from -2,000 mV to +2,000 mV. The higher the ORP is, the faster acting it is at disintegrating the biological contaminant or virus that we need removed. This means that it requires a lower dwell time or exposure time to the ozone to break down and disintegrate than many other cleaning agents and without leaving chemical residue as many others do. Ozone has an ORP of 2,070 mV and is one of the most effective substances on the planet as disinfecting.
Some specific compounds oxidized by ozone include:
- Amoebae
- Amonia
- Arsenic
- Bacteria on food & surfaces
- Cyanides
- Cigarette Smoke
- Detergents
- DDT
- Dioxins
- Fulvic Acid
- Haloforms
- Perchlorate Biphenyls
- Phenolics
- Spores of Molds
- Sulfides
- Trihalomethanes
- Trichlorophenol
- Oxidation Potential [eV]
-
Ozone 2.07
-
Peroxyacetic Acid 1.81
-
Hydrogen Peroxide 1.78
-
Hypochlorous Acid 1.49
-
Sodium Hypochlorite 1.36
-
Oxygen 1.23
-
Chlorine Dioxide 0.95
- eV
- 0
- 0.5
- 1
- 1.5
- 2
- 2.5
The bacteria and viruses found in the food supply outbreaks have specific ORP values required to kill them in certain timeframes. For example, E.Coli requires an ORP of 650-700 mV to kill it within 30 seconds.